Pharmacopoeia quality
Pharmacopoeia Quality
We stick to the book when it comes to quality. We test our botanicals using standard pharmacopoeia methods. And we design our processes to meet those global standards. It’s how we keep things consistent and reliable.
The pharmacopoeias provide the herbal industry with objective, transparent, scientifically validated methods for demonstrating quality. They represent the best collective knowledge available for ensuring botanicals are what we say they are, contain what we claim they contain, and are safe for human consumption. The USP (United States Pharmacopeia), European Pharmacopoeia, British Pharmacopoeia, and Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India all publish specifications or monographs for herbs. If an ingredient doesn’t meet these specs, we work to understand why not.
Why this matters
Suppliers often claim their herbs are 100% pure. They provide certificates to prove it. But we always ask: did they actually run the tests? And what methods did they use?
We see issues more often than you might expect. We have found high Withanolide Ashwagandha powder that was actually mixed with leaf powder instead of just root to spike the numbers. We have seen Turmeric powder containing artificial color or curcuminoids. Often the botanicals that look fine, fail when we examine them under a microscope or run a chemical analysis.
This is exactly why pharmacopoeias exist. They provide the standard testing methods to catch these shortcuts. By following them, we don’t have to rely on trust. We can verify exactly what is in the bag.
How we test
Every batch goes through four types of testing:
1. Identity: Is it the right plant?
We establish botanical identity through a tiered approach, starting with Macroscopic Identification. Whole herbs undergo morphological assessment, where physical traits are cross-referenced with Pharmacopoeial standards. Microscopic Evaluation follows this; we use both tissue sectioning and powder microscopy, we analyze diagnostic characters such as trichomes, stomata, and cell inclusions.
The final confirmation is achieved via HPTLC (High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography). By chromatographically separating the plant’s compounds, we obtain a unique chemical fingerprint. This profile is compared against a certified reference standard, ensuring that any deviation, indicating species substitution or adulteration, is immediately identified.
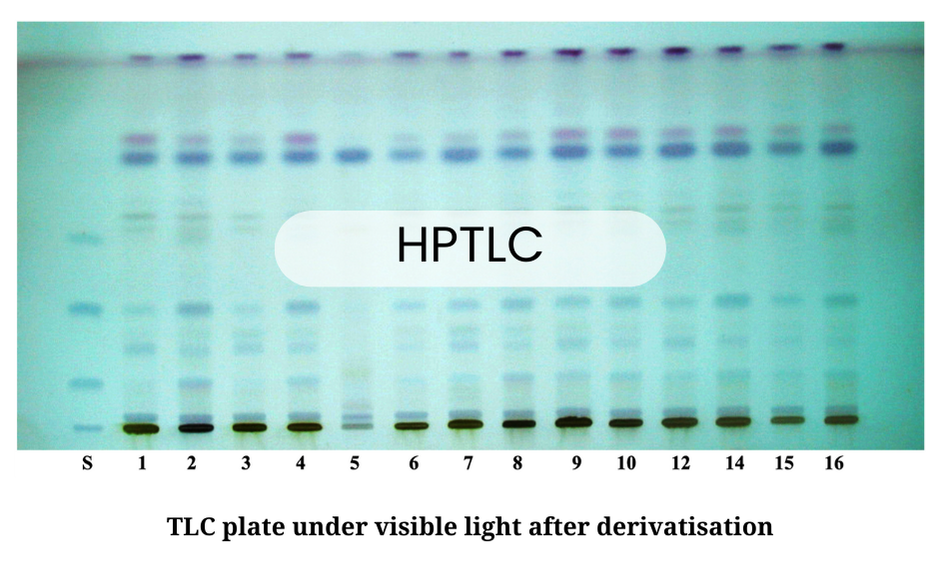
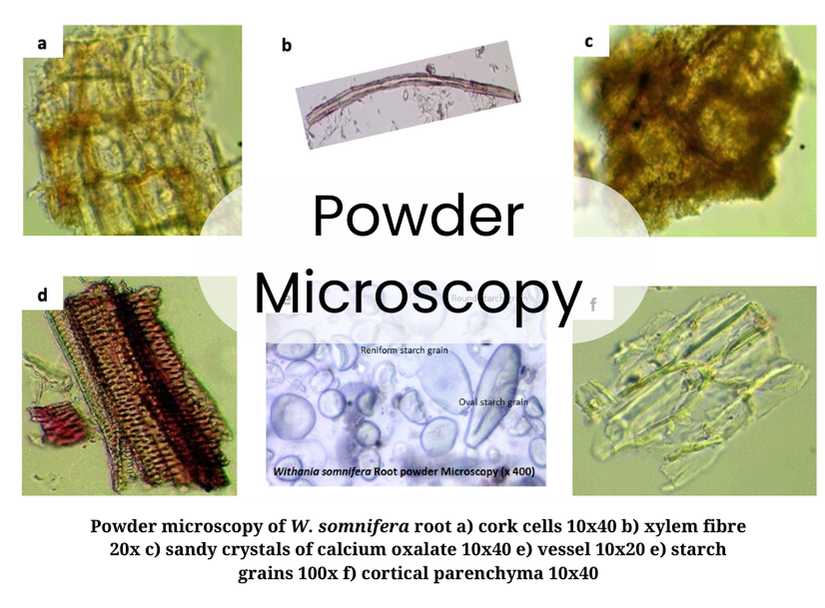

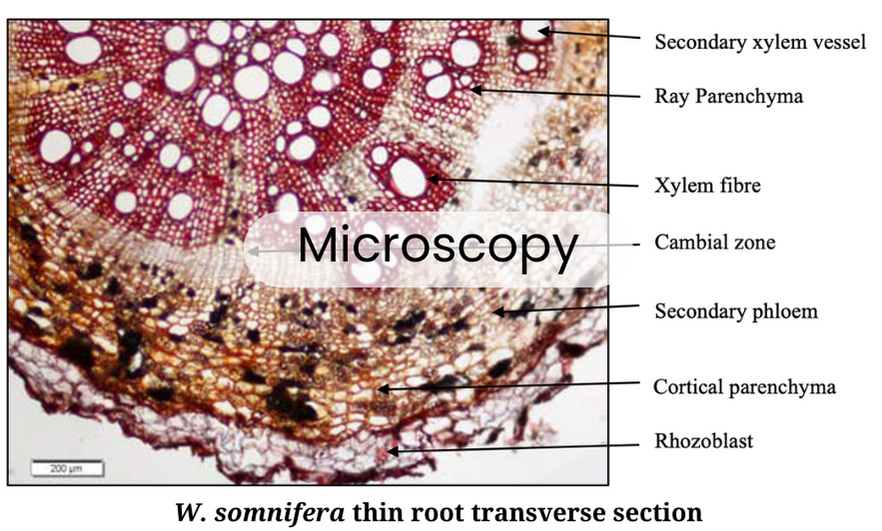
Our Lab
We have an ISO 17025 accredited laboratory. That means our testing methods are validated and our results are recognized by regulatory bodies worldwide.
Most suppliers send samples to outside labs and wait weeks for results. We run our own tests. This gives us faster answers and better control over quality.
One Standard for All Markets
Different countries use different pharmacopoeias. The US focuses on identity testing. Europe emphasizes purity. India includes traditional preparation methods.
Instead of creating different versions of each herb for different markets, we try to aim for the strictest requirement from any pharmacopoeia.
This means one batch can go to customers in the US, Europe, or Asia. You don’t need separate suppliers for different regions.
2. Quality: Does it have the right compounds?
We measure the marker compounds that are unique to each herb. We quantify the amounts using HPLC analysis.
For example:
- Ashwagandha: minimum 2.5% withanolides (the specific ones defined by USP)
- Turmeric: minimum 1.5% curcuminoids
- Brahmi: minimum 1.5% bacosides
- Gotu Kola: minimum 0.75% triterpenes
They’re based on pharmacopoeia standards and clinical research.
3. Purity: Is it clean?
We test every batch for:
- Pesticide residues (against European limits, which are stricter than most regions)
- Heavy metals (lead, cadmium, mercury, arsenic)
- Mycotoxins (from fungal contamination)
European Pharmacopoeia sets some of the toughest purity standards in the world. We try to use those as our baseline.
4. Safety: Is it free from pathogens?
Many sterilization methods: irradiation, ethylene oxide are prohibited under organic standards or consumer-rejected. We’ve developed processing protocols that achieve microbial compliance through:
- Source material selection and proper drying at source (sun or covered shade)
- Cold storage of fresh material followed by timely processing to minimize microbial proliferation
- 3rd-party validated microbicidal treatments compatible with organic certification
- R&D backed heat treatment that is unique to each herb.
Target: Total Aerobic Microbial Count <10⁴ CFU/g, pathogens absent.
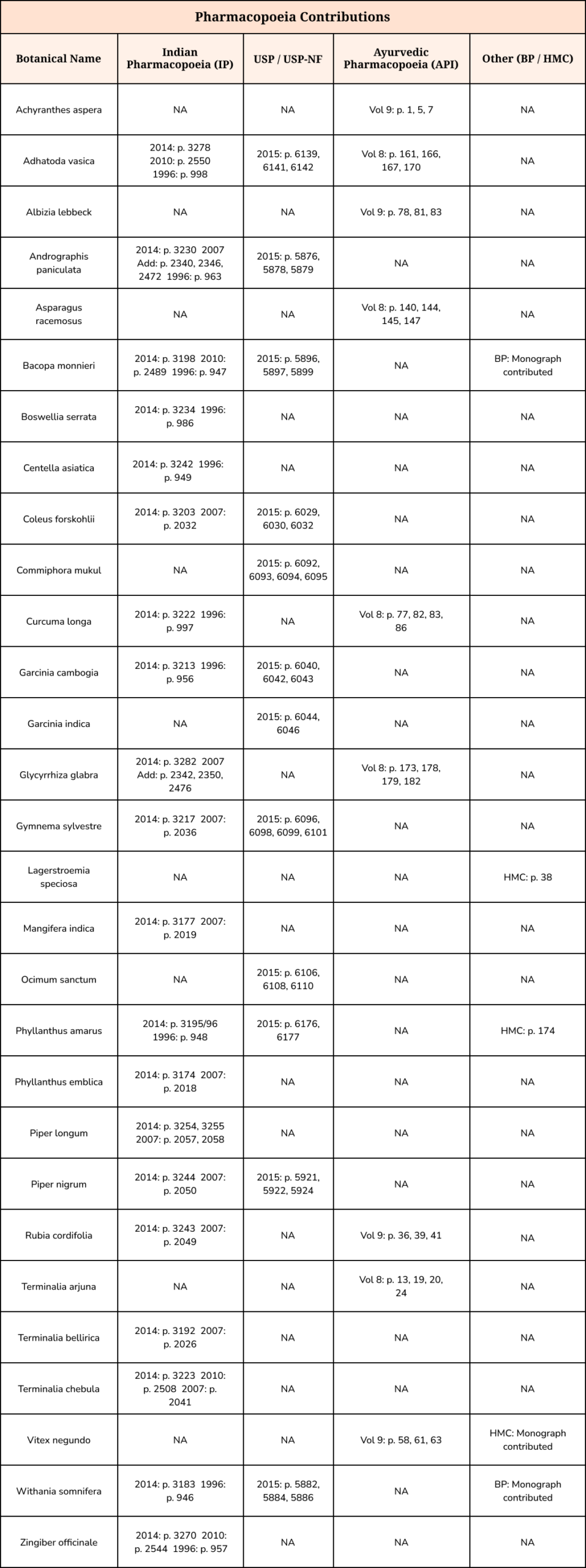
Setting Standard for Quality
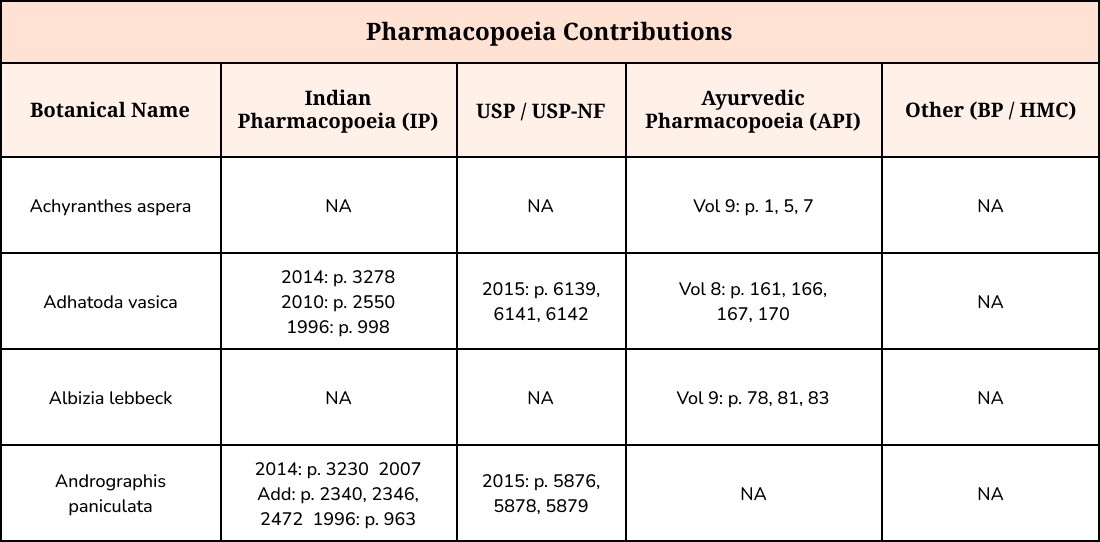
This table summarizes the analytical monographs contributed by your team to the Indian Pharmacopoeia (IP), United States Pharmacopeia (USP), Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India (API), and others.
Ashwagandha ID manual
As an example, we have published this identification manual. Submit your details to access the full document.


Why we do this
The botanical ingredients industry is characterized by inherent variability, inconsistent regulations, and trust deficits. In this landscape, the pharmacopoeia offers much-needed objectivity.
Related Blogs

Setting standards for quality
Discover Herb Artizan’s quality standards supported by in-house ISO 17025 certified testing and four testing pillars.

Our Process Is Our Strength
Learn about Herb Artizan’s process strength, utilizing smart equipment and 100% visual inspections for high-quality herbal processing.

Traceable Herbs: Seed to Ship
In today’s global herbal ingredient market, the distance between the farm and your finished product can be vast and complex. This complexity introduces risk—risk of…

Traceable Herbs: Seed to Ship
In today’s global herbal ingredient market, the distance between the farm and your finished product can be vast and complex. This complexity introduces risk—risk of…

Our Process Is Our Strength
Learn about Herb Artizan’s process strength, utilizing smart equipment and 100% visual inspections for high-quality herbal processing.

Setting standards for quality
Discover Herb Artizan’s quality standards supported by in-house ISO 17025 certified testing and four testing pillars.
